Fever is a common health issue in India, affecting millions yearly. It is a symptom rather than a fever disease, often indicating an underlying infection or medical condition. Understanding the types of fever and their symptoms can help in early diagnosis and effective treatment. This guide covers different types of fever, their causes, symptoms, and available treatments to ensure better healthcare awareness.
What is Fever?
The medical term for fever is “pyrexia.” It is a temporary rise in body temperature, usually in response to an infection, inflammatory condition, or immune responses. Normal body temperature ranges from 97°F to 99°F (36.1°C to 37.2°C). A fever occurs when body temperature rises above 100.4°F (38°C). Recognising different types of fever is crucial for proper treatment and management.
Common Types of Fever and Symptoms
Fever can be classified based on its duration, pattern, and underlying cause. Below are the most common types of fever, with some examples in India and their symptoms and treatment approaches.
1. Acute Fever
Definition: A fever that begins abruptly and lasts less than seven days.
Common Causes include viral infections (influenza, common cold), bacterial infections (strep throat, UTI), gastrointestinal infections, and respiratory infections.
Symptoms:
- A sudden increase in body temperature
- Fatigue
- Body aches
- Chills
- Cough and sore throat in some cases
Treatment:
- Adequate hydration
- Commonly prescribed fever medicine names in India are Paracetamol or Ibuprofen.
- Rest
- Seek medical advice if fever persists beyond three days.
2. Subacute Fever
Definition: A fever that lasts longer than an acute but shorter than a chronic fever, generally between one and two weeks.
Common Causes: Infections (bacterial, viral, fungal), autoimmune diseases, and some medications.
Symptoms:
- Persistent mild-to-moderate fever
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
Treatment:
- Blood tests to determine infection type
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Antiviral medications
- Corticosteroids
- Symptomatic care
3. Recurrent Fever
Definition: Fever that reappears at intervals after an afebrile (normal temperature) period.
Common Causes: Malaria, brucellosis (an infectious disease caused by brucella), periodic fever syndromes, and certain cancers (Hodgkin’s lymphoma).
Symptoms:
- Episodes of high fever followed by symptom-free days
- Sweating
- Headaches
Treatment:
- Diagnosis through blood tests
- Immunological tests for autoimmune causes
- Prophylactic antibiotics
- Antimalarial drugs if malaria is suspected
4. Chronic Fever
Definition: Fever that persists for more than three weeks.
Common Causes: Infections (tuberculosis, HIV), autoimmune diseases, cancers, inflammatory conditions.
Symptoms:
- Continuous low- or high-grade fever
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
Treatment:
- Thorough medical evaluation
- Long term antibiotics
- Specific treatment depending on the cause
5. Intermittent Fever
Definition: Intermittent fever means fever that comes and goes, with periods of normal temperature in between.
Common Causes of Intermittent Fever include malaria, septicemia, and certain bacterial infections (e.g., typhoid fever).
Symptoms:
- Cyclic fever pattern with chills
- Sweating when the fever subsides
Treatment:
- Antimalarial drugs
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Book Lab Test for diagnosis
6. Remittent Fever
Definition: A fever in which the temperature fluctuates but does not return to normal. There is a variation, but it stays elevated. A common remittent fever example is typhoid.
Common Causes: Malaria, sepsis, endocarditis
Symptoms:
- Constantly fluctuating fever levels
- Fatigue
- Sweating
Treatment:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Supportive care
7. Hyperpyrexia
Definition: Fever above 106°F (41.1°C) is considered a medical emergency.
Common Causes: Severe infections, heatstroke, brain haemorrhage, drug reactions, malignant hyperthermia.
Symptoms:
- Extremely high fever
- Seizures
- Confusion or unconsciousness
- Rapid breathing
Treatment:
- Immediate cooling measures
- Emergency medical intervention
8. Low-Grade Fever
Definition: Fever between 99.1°F to 100.4°F (37.3°C to 38°C).
Example:
Common Causes: Viral infections, early stages of some bacterial infections, inflammatory conditions, and post-vaccination reactions.
Symptoms:
- Slight elevation in temperature
- Mild fatigue
- Mild headache
Treatment:
- Usually, it doesn’t require treatment unless other symptoms accompany it.
- Symptomatic care
- Monitoring for progression
- Home remedies such as fluid intake and rest.
9. Relapsing Fever
Definition: A fever that returns after being afebrile (without fever). It’s distinct from recurrent in that the afebrile periods are more substantial.
Common Causes: Borrelia bacterial infections (tick-borne relapsing fever).
Symptoms:
- Recurrent fever in adults with chills
- Severe headache
- Joint pain
Treatment:
- Antibiotics
- Supportive care
10. Septic Fever
Definition: Fever caused by a widespread infection in the bloodstream.
Common Causes: Bacterial infection in the bloodstream (sepsis).
Symptoms:
- Persistent high fever
- Rapid heart rate
- Rapid breathing
- Low blood pressure
- Confusion
- Other signs of infections
Treatment:
- Immediate hospitalisation
- IV antibiotics
11. Drug-Induced Fever
Definition: A fever caused by an adverse reaction to a medication.
Common Causes: Allergic reactions to drugs like antibiotics and anticonvulsants.
Symptoms:
- Fever that appears after starting a new medication
- Rash, itching, or allergic symptoms
Treatment:
- Discontinuation of the suspected drug
- Consulting a doctor for alternatives
12. Idiopathic Fever
Definition: A fever of unknown origin; the cause cannot be identified even after extensive medical tests.
Common Causes: Unknown cause (diagnosis of exclusion).
Symptoms:
- Persistent fever with no clear diagnosis
Treatment:
- Regular monitoring
- Symptomatic care
- Rest
- Fluid
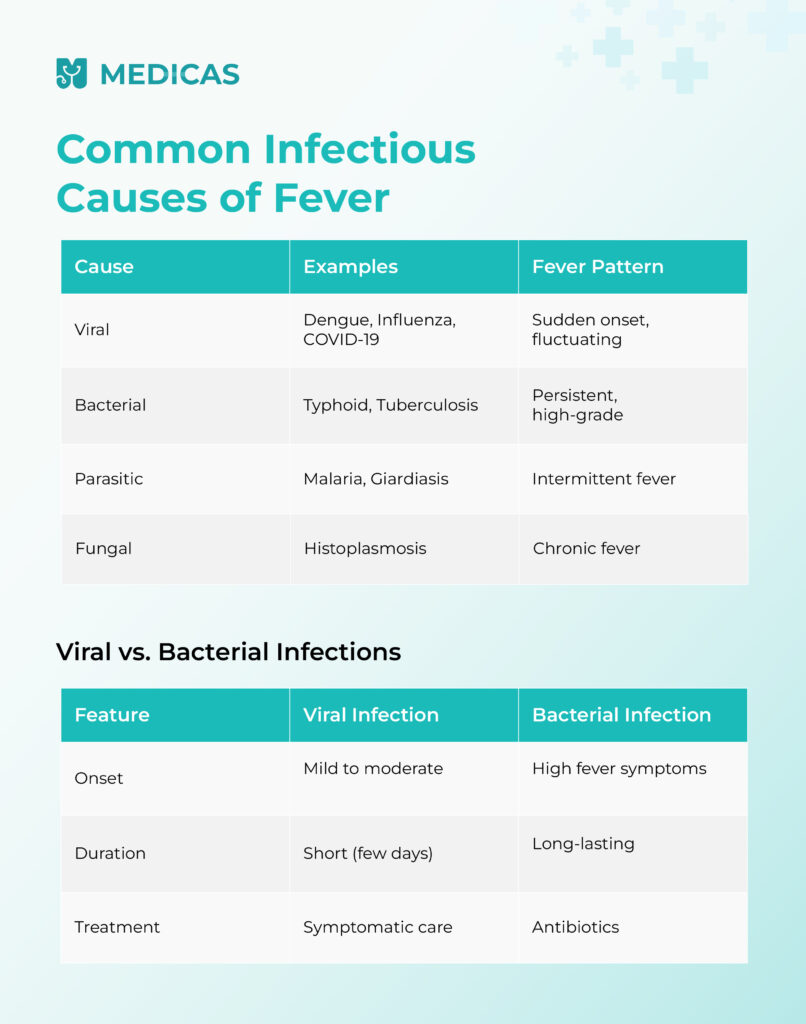
Understanding the Causes of Fever
Fevers can result from various infections, autoimmune disorders, or environmental factors.
Common Infectious Causes of Fever
When to Seek Medical Attention for Fever
While most fevers resolve independently with rest and home care, certain situations warrant immediate medical attention.
Signs When Fever Becomes a Medical Emergency
- High fever symptoms above 106°F
- Stiff neck
- Rash
- Persistent vomiting
- Seizures
- Confusion or altered mental state
- Breathing difficulty
- Severe dehydration (e.g. decreased urination, dry mouth)
- Symptoms of sepsis (low blood pressure, rapid breathing)
Conclusion
Understanding fever classification is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Consulting a doctor early can help in effective management. Medicas provides easy access to Online Doctor Consultation and Book Lab Test services for timely intervention. If you’re experiencing prolonged fever, book an online doctor appointment through Medicas today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fever
What are some common fevers associated with infections in India?
Some common types of fever related to infections in India include typhoid, dengue, malaria, and chikungunya.
How does an online medical booking system improve patient access to healthcare?
Medicas’ Online Doctor Consultation system instantly helps patients connect with specialists, reducing travel time and ensuring prompt treatment.
What are the benefits of using an online appointment system for doctors and patients?
- For Patients: Quick access to specialists, hassle-free bookings
- For Doctors: Streamlined scheduling, better time management
How can I book a medical appointment online with a specialist?
You can Book Appointments via Medicas’ website or app, choose a specialist, and schedule a consultation from the comfort of your home.
Related Blogs
Disclaimer
Medical Advice: The information provided in this blog post is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance regarding your specific medical condition.
Accuracy of Information: While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, the field of medicine and viral fevers is constantly evolving. The content in this blog post may not reflect the most current research or medical guidelines. Therefore, it is advisable to cross-check any information provided with reliable sources or consult a healthcare professional.
Individual Variations: The symptoms, causes, treatment options, and preventive measures discussed in this blog post are general in nature and may not apply to everyone. It is important to remember that each individual’s situation is unique, and personalized medical advice should be sought when making healthcare decisions.
External Links: This blog post may contain links to external websites or resources for additional information. However, we do not endorse or have control over the content of these third-party websites. Accessing these links is done at your own risk, and we are not responsible for any consequences or damages that may arise from visiting these external sources.
Results May Vary: The effectiveness of treatment options or preventive measures mentioned in this blog post may vary from person to person. What works for one individual may not work the same way for another. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice tailored to your specific needs.



